I. Introduction
As an essential piece of equipment, the press brake plays a pivotal role in metal sheet fabrication. It is mainly designed for achieving metal sheet precise bending and forming.
It is widely used in various precision machinery industries such as automobile manufacturing, aerospace, electrical appliance manufacturing, etc., which can ensure the products’ precision and production efficiency.
However, there is always a problem that the press brake won’t go up, troubling many sheet metal enterprises.
This problem may not only cause production stagnation and delivery delays but also directly affect the quality of the workpiece, increasing unnecessary repair costs and production losses.
Our passage aims to offer a comprehensive solving guide for this troublesome issue.
We will delve into the various reasons why the press brake won’t go up, and combine the abundant sheet metal knowledge ranging from equipment maintenance, and operation regulations to malfunction troubleshooting, to talk about how to solve this problem, making the operation stable and efficient and the overall the procedure smooth and effective.
II. Understanding Press Brakes
Basic Components of a Press Brake
Press brake is mainly composed of the following basic components: body frame, hydraulic system, electric control system, back gauge device, tooling (upper punch and bottom die), and worktable.
The body frame is the basic structure of the equipment, the hydraulic system is responsible for the pressure required by bending, electricity control system can ensure the precision and automation degree of the equipment operation.
The back gauge is designed for positioning the sheet, and the tooling determines the shape and size of the workpiece, while the workbench is designed for supporting and fixing the sheet to be processed.
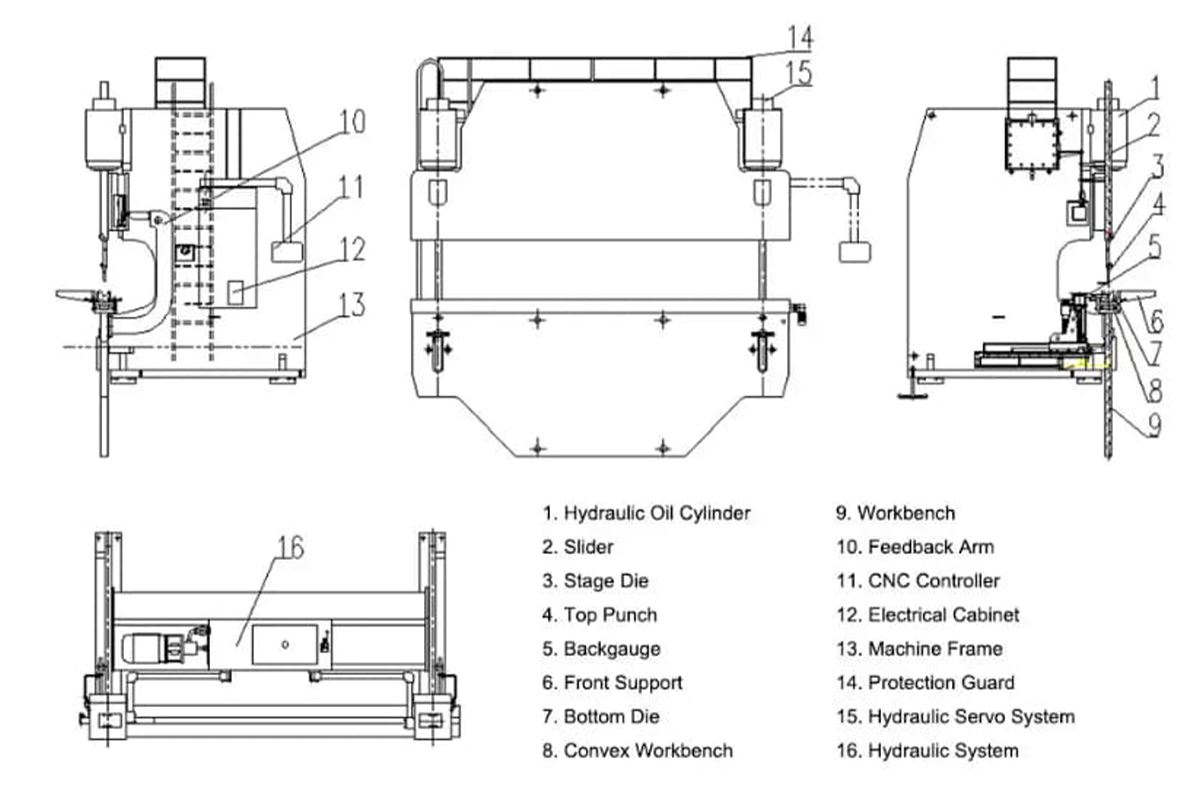
How Press Brakes Function in Metal Fabrication
In metal fabrication processing, the press brake plays an important role, which is assisted by strong hydraulic pressure, and can precisely bend the flat metal sheet into the required 2D or 3D shapes through adjusting the angle and distance between the upper and bottom die, achieving the high efficient forming processing of the components.
This process is of decisive significance for manufacturing various sheet metals, like boxes, shells, and brackets.
Significance of Press Brake Maintenance
The stability and lifespan of the press brake are mainly determined by daily maintenance.
Work like regular lubrication, cleaning, checking, and replacing abrasive components can effectively avoid malfunction situations occurrence won’t go up because of aging, abrasiveness, blocking, etc.
Besides, good habits of maintenance can ensure press brake precision, lower production errors, improve production quality, prolong the equipment lifespan, and reduce downtime and maintenance costs, which is beneficial for enterprises’ consistent and highly efficient production.
III. Common Issues in Press Brake Operations
Overview of Common Press Brake Problems
Many problems occur in press brake operation, including precision errors due to lack of hydraulic system pressure, tooling worn or improper installation, and movement incoordination, the inaccurate position of the back gauge owing to electrical control system malfunction.
Our passage is mainly focusing on one of the common situations--press brake won’t go up.
When the press brake won’t go up, this may be caused by one of the key procedures in the equipment's inner step.
This problem leads to the entire sheet metal processing process coming to a standstill, severely affecting the production efficiency and production quality.
Initial Diagnosis: Steps to assess the problem
It is paramount to proceed with the initial diagnosis that the press brake won’t go up. The operator should troubleshoot according to the following procedures:
Check whether the oil level of the hydraulic system is common or not and whether the oil leaks or oil blocks.
Ensure the power supply and signal transmission of the electrical control system is smooth or not. Check the related button, switch, and contact working situation.
Observe and test if the equipment has abnormal noise or vibration to check if the mechanical component is damaged or stuck.
Mechanical vs. Electrical Issues
The reason for “press brake won’t go up” may be divided into two main types: mechanical and electrical problems.
A mechanical problem is concerned with the components worn, torn, or blocked, like hydraulic cylinders, pistons, connecting rods, bearings, and so on, and seals failure and oil circuit blockage in the hydraulic system.
Electrical problems are derived from the failure of electrical components like a controller, motor, relay, sensor, or poor contact, short circuit, open circuit, etc. in the power supply line.
Safety Precautions
Ensuring safety is a priority to other tasks in press brake troubleshooting procedures. The operator must obey the related working regulations.
For example, how to check the electrical in a power outage state, how to use specialized tools to touch the movement components directly instead of fingers, and set the warning signals before repairing to avoid other people operating incorrectly.
Only obeying the safety regulations can solve the problem efficiently and ensure the operator's and equipment's safety.
IV. Mechanical Causes and Solutions
Hydraulic System Malfunctions
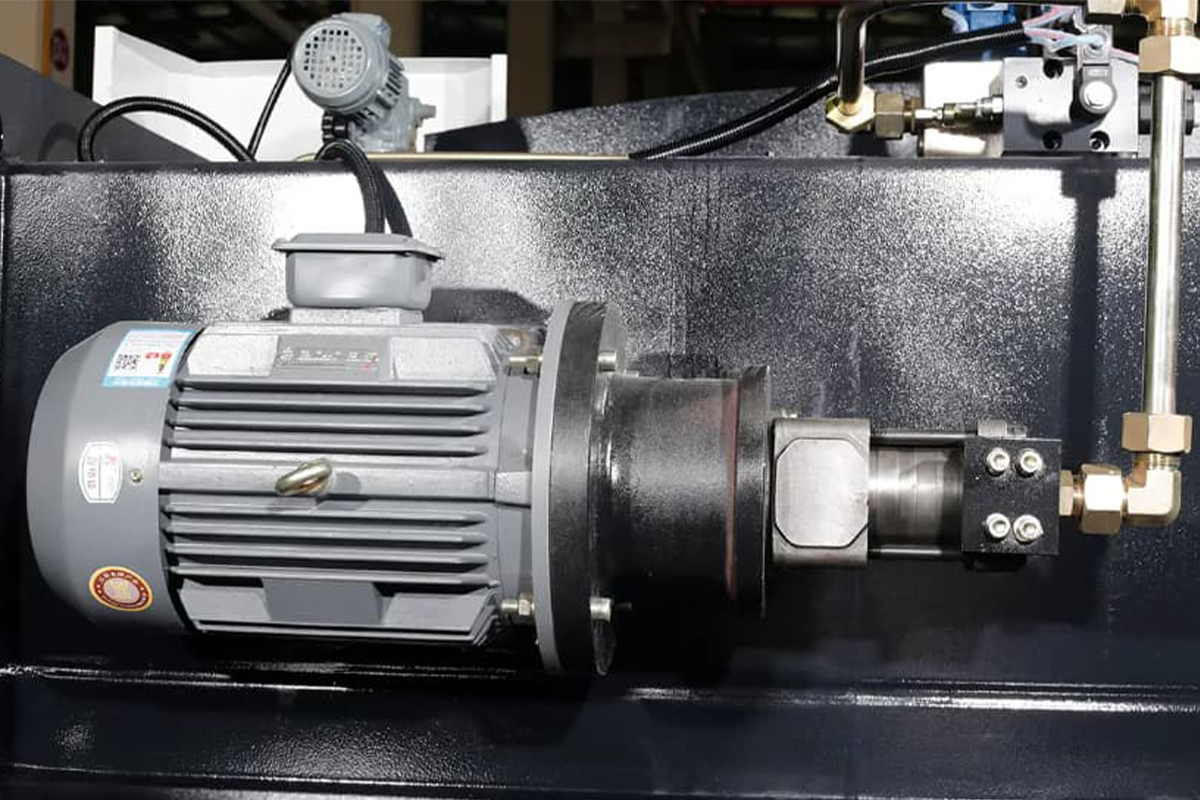
- Hydraulic oil leakage: hydraulic oil leakage may be caused by seals worn or damaged. Regular checking and replacing seals and keeping hydraulic oil clean is the key. If the leakage is found, repair it immediately, and ensure the hydraulic oil is added correctly.
- Hydraulic pump: the hydraulic pump is the heart of the hydraulic system. The failure may result from the pump being worn or pressure lack. Regularly check the state of the hydraulic pump, replace the components when necessary, and ensure the pressure is within normal range.
- The hydraulic line blocked: the blocked hydraulic line affects the flow of the fluid, resulting in machine performance decreasing. Regular cleaning and maintaining the hydraulic line ensures the hydraulic fluid is smooth.
Mechanical Failures
- Bending rod problem: press brake bending rod bears large pressure and stress. The rod's abrasiveness and damage probably lead to inaccurate bending. Regularly check the press brake bending rod, making sure it is in good condition, and replace it when necessary.
- Ram and guide rail failure: ram and guide rail are important parts of the press brake, which are responsible for keeping the material stable. Damage or incorrect lubrication may lead to ram blocking or offset the rail. Regularly lubricating and checking the state of the ram and guide rail is the key to precaution the problem.
- Electrical component failure: mechanical failures are probably related to electrical components, like motors, sensors, or controllers. Regularly check electrical system connectivity and status, ensuring all the operation is normal.
Regular Maintenance Tips
- Checking regularly: establish a regular machine checking plan, including the mechanical system, mechanical components, and electricity system. Finding the problem early and repairing instantly can avoid mass-scale failure.
- Cleaning and lubricating: keep the machine clean, and lubricate the hydraulic system and mechanical components regularly to avoid friction and abrasiveness.
- Training the operator: ensure the operators accept the proper training, know the machine's normal movement and possible failure situation, and how to take appropriate approaches.
V. Electrical Causes and Solutions
Electrical Component Failures
- Cable and wiring issues: the cable may be broken, poorly connected, or damaged, resulting in electrical malfunction. Check the integrity of cable and wire, ensuring their safe connection without wear or damage.
- Electrical components aging: Long-time use and abrasiveness may lead to electrical aging, such as relays, switches, and cable plugs. Check the state of the electrical components, and replace the aging ones when necessary.
- Power problem: power supply problems, such as voltage unstable or current load overloading, lead to electrical failure. Ensure all the equipment can be connected to stable power, and use the power protective equipment according to your needs.
Troubleshooting Electrical Issues
Shut down and ensure safety: the power supply must be cut off before maintaining any electrical issues to assure the operators’ safety.
Preliminary judgment: judge the probable trouble area preliminarily according to failure phenomenon (equipment unstarting, unusual movement, alarm displaying).
Detailed checking: check the probable malfunction area in detail. Check whether the connector is loose, the cable is damaged, and switches, relays, contactors, and other components are intact.
Test and verify: use the test tools to test the suspected components singly or combinationly to ensure the failure source.
Repair and replace: once the malfunction point is found, repair or replace the damaged electrical components in a timely, and restore the system's normal operation.
Preventative Electrical Maintenance
- Checking regularly: establish a plan for checking the electrical components’ state, including cable, plug, relay, and switch.
- Cleaning and maintenance: keep the electrical components clean, and avoid debris or dust accumulation. Clean the cable, plugs, and relay contacts.
- Electrical training: offer basic electrical training for the operators, making them recognize the common electricity problem and adopt the appropriate approaches.
VI. Software and Control System Errors
Identifying Software-Related Issues
- Abnormal operation interface: if your press brake operation interface displays abnormal or false information, this may be an obvious software problem phenomenon.
- Control system in reaction: when the equipment is started or stopped, if the control system doesn’t react or react slowly, this may be caused by software failure.
- Output unstable: abnormal output, such as unstable bending angle or size, which may result from the control system or software.
Resetting and Updating Control Systems
- Reset the system: try to reset the control system, which can be achieved by closing the power, waiting for a few minutes, and resetting. This can clear some instant problems.
- Update the software: check whether there is available software to be upgraded. The manufacturer usually releases fixed and improved software versions. The known problems can be solved by upgrading.
- Restore default settings: if the software problem can not be solved, the control system can be restored to the factory default settings, and reset it.
When to Seek Professional Help for Software Problems
- Problems can not solved: manufacturers or professional support may needed if the problems are still here after the above procedures are tried.
- Safety problem: if the software problem threatens the safety of operators or breaks the equipment, the equipment should not be used, and assistance is needed.
- Authorized maintenance personnel: it is better to connect the authorized maintenance personnel or manufacturing technique supporting teams to handle the software or control system problems when the relevant skills and knowledge are short.
VII. Advanced Troubleshooting Techniques

Using Diagnostic Tools
Hardware diagnostic tools: such as portable oscilloscopes, digital multimeters, and infrared thermal imaging cameras, can be used to measure electrical parameters like voltage, current, and frequency, and check the circuit's moving state. Meanwhile, thermal imaging cameras can reflect the equipment's fever, helping to discover overheating or poor heat dissipation.
Software diagnose systems: many modern press brakes and sheet metal equipment are equipped with inner malfunction diagnose software, which can monitor the system state and record false codes. The operator can quickly position the potential point of failure by reading false codes and warning information, and combining the equipment manual to do the preliminary analysis.
Internet and communication diagnose tools: as for the equipment adopting a digital control system, and using specialized internet diagnose tools to check the stability of the communication links, ensuring the controller, sensor, and driver’s data transformed is abnormal.
Remote diagnose service: some high-tech equipment offers a remote diagnose function, allowing the manufacturing technique teammates to be directly linked into the equipment control system through the internet, checking the equipment state, log files, and real-time data remotely, achieving quick and precise questions positioning.
Consulting Technical Support
- Complex questions: if the question is very complex, and exceeds your technology sphere, it is better to consult the manufacturing technique support and professional maintenance personnel.
- Under warranty: if the equipment is still under warranty, it is better to seek manufacturing for support, to make sure the problems can be solved under warranty.
- Safety questions: if the question is related to the safety of the equipment, such as electrical problems or mechanical problems may lead to danger. Stop the equipment immediately and search the professional seek professional help.
- Professional advice: if the problems remain after the methods are tried, consult the professional support for advice and solutions.
VIII. Conclusion
Our passage deeply talks about the troubleshooting and performance optimization of the press brake and sheet metal equipment, emphasizing analyzing the common issues and solutions of the hydraulic system, mechanical equipment, electrical system as well as software control.
Through maintaining the good condition of the equipment and the high-level technique skills of the operator, you can largely minimize downtime, reduce repair costs, and improve stability and competitiveness.
So, investing in maintenance and training is the key to ensuring the successful operation of the press brake and sheet metal equipment.
Welcome to browse the ADH machine tool official website for info searching and machine purchasing.