The CNC press brake is a sophisticated sheet metal processing machine that requires precise operation under the control of both a CNC controller and an operator.
It is important to carefully set the necessary parameters and procedures before beginning a bending job.
However, even with proper preparation and maintenance, the press brake can still experience mechanical failures over time.
Common issues include vibrations during bending, oil leaks, and inaccurate size and shape of the finished workpieces, leading to material waste and even damage to the machine.
In some cases, these faults can also pose a risk to the safety of the operator.
In this blog, we will explore the reasons for errors in press brake bending and offer tips on how to prevent and avoid them.
The machine is not kept clean.
Neglecting to keep the press brake clean is a common issue in its usage.
Over time, accumulated dirt can cause parts and molds to wear down.
Debris can even scratch the workpiece and the presence of dust can impact the machine's operation.
To prevent these issues, it is important to clean the press brake and its tools both before and after use.
All debris, oil, and dust should be removed to prevent dust from infiltrating the machine.
Regular cleaning can extend the machine's lifespan.

The ram is not vertical when running
The wear and tear of the guide rail and inadequate lubrication over time can lead to increased clearance.
It is essential to inspect the degree of wear on the guide rail and adjust the clearance accordingly.
If the wear is significant, the guide rail pressing plate needs to be replaced.
Failure to lubricate the press brake on time can exacerbate friction between moving parts.
To prevent untimely lubrication, it is recommended to use an automatic or semi-automatic lubrication system.
To ensure the longevity of the press brake, it is best to choose a tin bronze plate or ductile iron with a joint surface that is ground.
The connecting bolt should be positioned below the joint surface and have a serrated lubricating oil groove to promote efficient lubrication.
Ram upset
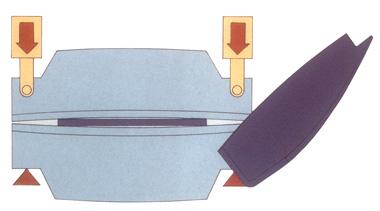
Long-term bending can cause the press brake's ram and the center of the worktable to bulge.
This protrusion, known as deflection, refers to the upward protrusion of the ram and downward bending of the center of the worktable under maximum tonnage load.
Deflection is limited by the maximum tonnage load, and the ram and worktable can return to their normal positions if the load is removed.
However, if the ram and worktable are defective and the tonnage load is too high, it may cause temporary or permanent damage to the center of the ram and worktable.
This results in a larger distance between the center of the ram and base compared to the distance at both ends, causing the angle of bending at the center to be greater than the angle of bending at both ends.
This defect can impact the accuracy of bent workpieces and result in a canoe-like shape.
To mitigate this issue, it is recommended to gradually adjust the load within the machine's rated tonnage range, equip the machine with a crowning device, and use shims to offset the deflection of the ram.
If compensation is no longer possible, the only solution is to remachine the ram and worktable.
The ram cannot move down quickly / slowly
If the ram's movement is too slow when it moves down, it may be due to the tightness of the guide rail or a lack of signal from the servo valve.
Another possible cause is that each axis of the back gauge is not properly adjusted.
Additionally, the ram may not return to the top position due to a stuck filling valve or a leaky sealing ring.
To troubleshoot this issue, it is important to check the appropriate tightness of the ram guide rail and to ensure that the servo proportional valve has an electric signal.
Additionally, the axis of the back gauge should be checked to ensure it is in place according to the programming of the controller.
Finally, the filling valve should be checked for any signs of being stuck, as well as for any leaks in the sealing ring.
Incorrect bending radius
An incorrect bending radius can cause damage to tooling and result in inaccurate bending of the workpiece.
This can occur when the bending radius is too small and the pressure on the die tip becomes excessive, or when the opening of the workpiece is too close to the bending radius.
To avoid damage to the tooling and workpiece, the following measures should be taken:
- Determining the bending radius based on the material specifications for each process.
- Understanding that the bending radius for longitudinal bending is larger, while the bending radius for transverse bending is smaller.
- Ensuring that the distance between the plate opening (such as a notch) and the bending line is at least three times the thickness of the plate to prevent deformation of the workpiece.
Different materials have varying degrees of ductility and tensile strength, so it is important to consider these factors when determining the bending radius.
The main motor cannot be started
The failure of the main motor can be caused by loose wiring or a faulty control power supply.
Additionally, it is important to ensure that the emergency stop button has not been engaged.
Other potential causes include damage to the AC contactor, circuit overload, or a faulty thermal relay.
To troubleshoot this issue, check the wiring of the switch power supply, verify that the emergency stop button has been released, and ensure that there is adequate overload protection in the circuit.
Additionally, inspect other parts for damage.
The workpiece is cracked and uneven after bending
After bending, cracks may appear on the surface of the workpiece.
This can be due to a small inner bending radius of the die or a small bending gap.
The material itself may also be defective, with burrs facing outwards.
The curved end of the workpiece may also become uneven, which is due to the shrinkage and deformation of the outer surface after stretching, and the folding and deformation of the inner surface after compression.
To remedy these issues, it is necessary to improve the smoothness of the tools and increase the bending radius of the die.
Adjusting the bending gap and using metal materials with better plasticity can also help.
Ensure that the fillet radius of the die corresponds to the external fillet of the part.
The hydraulic system has no bending pressure
The cause may be due to blockages in the throttle hole and valve element or a leak in the piston sealing ring of the cylinder.
To resolve this issue, check if the throttle valve and valve element are blocked and clean any blockages promptly.
Ensure that the filling port of the oil tank is filled with hydraulic oil and that the tank is completely filled to vent any gas.
Inspect the piston sealing ring for leaks and replace it as needed.
Conclusion
We have discussed some common problems and solutions for press brakes.
There are many issues that can arise with press brakes, and not all of them can be listed here.
If you require further information, please feel free to contact us for more detailed answers.
Proper maintenance is crucial for the efficient use and prolonged service life of a press brake.

FAQs
How to calibrate the bending angle?
To calibrate the angle of the press brake, it is necessary to first calculate the bending force required to bend the metal sheet using a calculation formula.
Next, calculate the value of the indicated pressure (P) and adjust the force of the overflow valve handwheel to slightly exceed the force required for bending the metal plate.
The distance of the back gauge can be adjusted to change the positioning during bending in the length direction.
The position of the ram can be adjusted by changing the parameters on the controller, and the speed of the ram can be altered through the stroke switch.
The stroke time can be adjusted through the use of a potentiometer.
Finally, adjust the gap between the upper and lower toolings by using the button located at the lower right of the workbench.
How to calibrate the backgauge?
If the backgauge bar is inaccurate, it needs to be aligned and calibrated. To do this, first loosen the fastening bolts under the backgauge bar.
Next, adjust the front and rear screws and move the rear backgauge wheel forward until it is parallel.
Use a probe to check and measure the values on the left and right sides.
Then, loosen the front and rear flat head bolts and measure the value to ensure that the backgauge and probe are parallel.
Finally, adjust the X-axis datum to the correct size by programming the controller parameters.
What are the types of bending methods used on the brake press?
The press brake uses three bending methods: air bending, bottom bending, and coining.
In air bending, the punch only contacts the plate at the bottom die shoulder and the deeper the punch descends, the sharper the bending angle becomes.
In bottom bending, the top of the punch is in contact with the metal plate, and the tonnage required is small, causing the plate to rebound.
A sharp angle must be used to obtain the required bending angle.
Coining bending is derived from previous coinage technology and requires a very high tonnage, causing the die and plate to be in full contact.